VAW Mechanisms
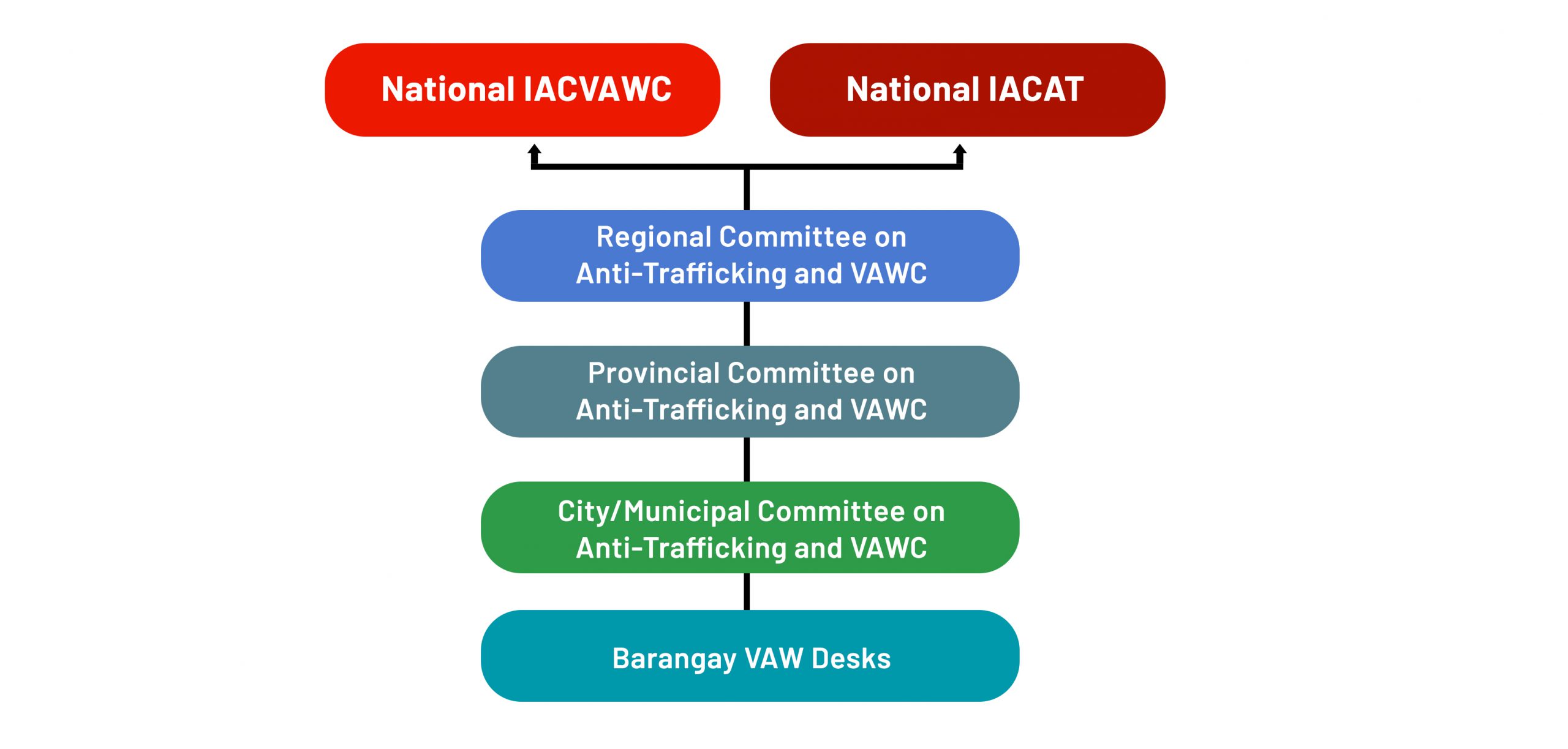
Pursuant to the Implementing Rules and Regulations of RA 9208 (Section 13) and RA 9262 (Section 59), different VAW mechanisms were established in support of the national IACs (i.e., Inter-Agency Council Against Trafficking (IACAT), Inter-Agency Council Against Child Pornography (IACACP), and the IACVAWC), to properly cascade and implement the anti-VAW programs and services from the national to the local level.
Law enforcement and other service providers addressing VAWC, trafficking in person, and child pornography generally originate from the same network. Hence joint committees were established for expediency and to prevent duplication of functions/representation at the subnational levels.
They are categorized based on level of governance:
Regional Committees Against Trafficking and VAWC (RCAT-VAWCs)
DSWD Administrative Order No. 02-2013 instructs all DSWD Field Offices to establish and strengthen the Regional Committees against Trafficking and VAWC (RCAT-VAWC). It serves as the link between the national Inter-Agency Councils (IACs) and its subnational committees. Similar to the national IACs, Regional Committees are generally chaired by DSWD Regional Directors, with DILG Regional Directors serving as co-chairs. To date, all DSWD Field Offices have established respective RCAT-VAWCs operated by Led Secretariats, with the following functions:
- Monitor and ensure the implementation of the law in all regions;
- Localize anti-VAW laws, directives, and programs;
- Mobilize regional units and partner organizations;
- Submit accomplishment reports to the national IACs; and
- Provide technical assistance to local committees.
Local Committees on Anti-Trafficking and Violence Against Women and their Children (LCAT-VAWC)
As counterpart to the Regional Committees, the DILG, DSWD, and DOJ issued Joint Memorandum Circular 2010-01 ordering the creation of Local Committees on Anti-TIP and VAWC or LCAT-VAWC. This aims to further devolve and cascade the law’s implementation to the ground, through the facilitation of Local Government Units in the provincial, city, and municipal level.
The LCAT-VAWC is an umbrella term for subnational mechanisms, namely: the provincial- (PCAT-VAWC), municipal- (MCAT-VAWC), and city-level (CCAT-VAWC) committees and are chaired by the respective Local Chief Executives. All are directed to collaboratively address trafficking and VAWC-related concerns and provide assistance to TIP and VAW victim-survivors.
- In particular, they are tasked to:
- Monitor and ensure the implementation of the law at the local level;
- Address TIP and VAWC-related concerns within their level of governance;
- Encourage relevant NGOs and people’s organizations to assist in the formulation and conduct of localized interventions;
- Submit accomplishment reports to the RCAT-VAWC; and
- Provide technical assistance to local service providers and other mechanisms.
LCAT-VAWC Functionality as of CY 2022*
*Based only from reports submitted to DILG
As of 2022, only 4% of the LCAT-VAWCs that have submitted their assessment reports to DILG have remained at the basic level. 13% qualified as progressive, 32% as mature, and 51% as ideal.
| Localize, monitor, and ensure the implementation of TIP- and VAW-related laws, directives, and programs in the region | Monitor and ensure the implementation of TIP- and VAW-related laws, directives, and programs in the locality | |
| Monitor and oversee the implementation of P/LCAT-VAWCs; | Institute policies and programs to: protect victim-survivors, strengthen surveillance, investigation, and rescue systems, and ensure effective and efficient coordination | |
| Mobilize regional units and partner organizations; | Address TIP and VAWC-related concerns within their level of governance and encourage relevant NGOs and CSOs to assist in the formulation and conduct of localized interventions | |
| Manage a unified documentation system of served VAW cases | Undertake advocacy campaigns | Ensure establishment, functionality, and monitoring of VAW Desks in every Barangay |
| Submit quarterly reports to the Chairpersons of national IACs | Submit accomplishment reports to the RCAT-VAWC | |
| Provide technical assistance to LCAT-VAWCs | Provide technical assistance to local service providers and other mechanisms. | |
Barangay Violence Against Women (VAW) Desks
Section 12 D, Rule IV of the Rules and Regulations Implementing the Magna Carta of Women (Republic Act 9710) mandates the establishment of a VAW Desk in every barangay. VAW Desks serve as the frontline responder for VAW cases at the community level. It is operated by VAW Desk Officers designated by the Punong Barangay and is assigned to address all cases in a gender-responsive and sensitive manner. The guidelines for establishing and maintaining the VAW Desk are provided in Joint Memorandum Circular No. 2010-2 issued by DILG, DSWD, DOH, DepEd, and PCW. The Commission also published the Barangay VAW Desk Handbook to serve as a handy, reader-friendly reference for barangay officials and other local service providers.
In particular, the VAW Desk must perform the following functions:
- Respond to gender-based violence cases brought to the barangay;
- Record the number of gender-based violence handled by the barangay and submit a quarterly report to the DILG City/Municipal Field Office and the City/Municipal Social Welfare Development Office (C/MSWDO);
- Keep VAW case records confidential and secured, and ensure that only authorized personnel can access them;
- Assist victims of VAW in securing Barangay Protection Order (BPO) and access necessary services;
- Develop the barangay’s gender-responsive plan in addressing gender-based violence, including support services, capacity building, and a referral system;
- Coordinate with and refer cases to government agencies, non-government organizations (NGOs), institutions, and other service providers as necessary;
- Address other forms of abuse committed against women, especially senior citizens, women with disabilities, and other marginalized groups;
- Lead advocacies on the elimination of VAW in the community; and
- Perform other related functions as may be assigned.
Barangay VAW Desk Functionality as of CY 2022*
*Based only from reports submitted to DILG

